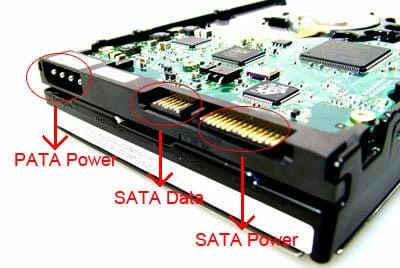
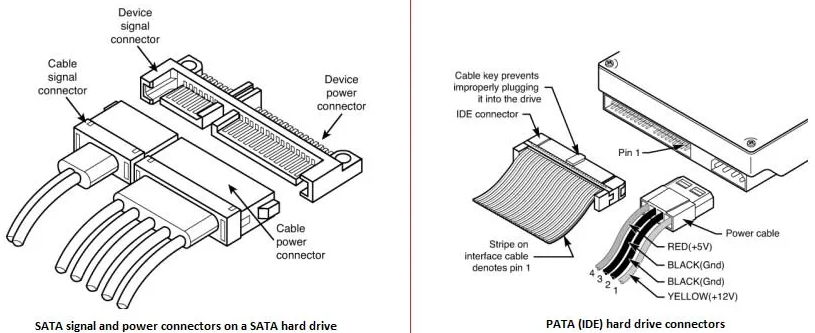
A SATA hard drive is a kind of rewritable mass storage device that is compatible with almost all computer motherboards and operating systems. It is distinguished by its good storage capacity, respectable transmission speeds, and faultless support.
Servers, laptops, and desktop PCs all contain SATA hard drives. Because SATA hard drives tend to produce a distinctive noise when reading or writing data, it's usually straightforward to identify that your computer has one.
Often known as 3.5-inch hard drives, SATA hard drives for desktop computers are normally 4 inches wide, 1.03 inches tall, and 5.79 inches long. Usually referred to as 2.5-inch hard drives, SATA hard drives used for laptops are 2.7 inches wide, 0.37 inches height, and 3.96 inches long.

SATA Hard Drive Definition and Technical Details
The Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) specification that the PATA interface uses has been improved upon in the SATA interface. SATA cables are easier to use and store since they are lighter and thinner than the bulky ribbon-type wires needed for the PATA interface.